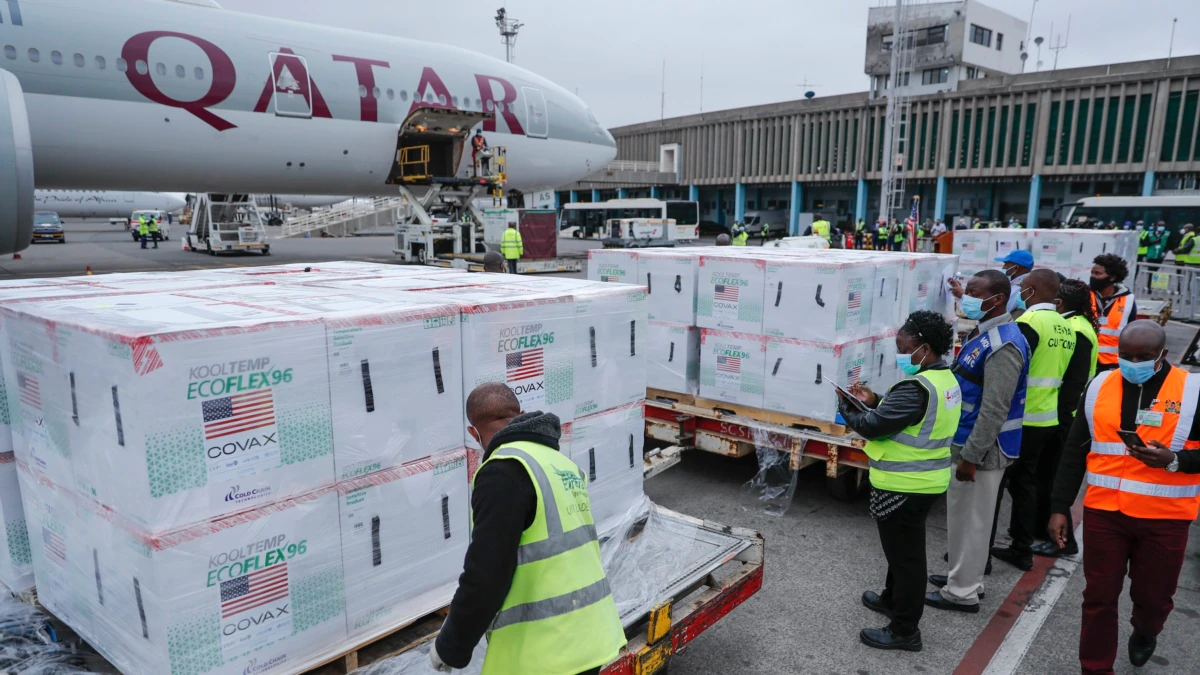
A Financial Times report says COVAX, the global collaboration established to ensure that poor countries have access to the COVID-19 vaccine, has “largely failed.”
“Wealthy countries have received over 16 times more COVID-19 vaccines per person than poorer nations that rely on the COVAX program backed by the World Health Organization,” the newspaper reported.
Millions of people in the world’s poorest countries have not yet received their first shots of the vaccine, while people in the wealthiest countries have access to booster shots, following their initial inoculations.
The disparity, The Financial Times warned, “could lead to a rise in cases and the emergence of more virulent strains, and hold back the global economic recovery.”
The World Health Organization’s director-general said Friday 82 countries are at risk of not meeting WHO’s goal of having 40% of every country’s population vaccinated against COVID by the end of the year. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said, “For most of those countries, it’s simply a problem of insufficient and unpredictable supply.”
Earlier this month, Britain reported its highest daily number of COVID-19 related deaths since March 9. A government advisor told a BBC television show Saturday that people should not wait for government mandates to begin initiating measures to prevent the transmission of the coronavirus.
Peter Openshaw, a member of the New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group, told BBC Breakfast, “I think hospitals in many parts of the country are barely coping actually” under the weight of COVID cases.
“The sooner we all act,” Openshaw said, “the sooner we can get this transmission rate down and the greater the prospect of having a Christmas with our families.”
British Prime Minister Boris continues to dismiss calls for renewed COVID-19 restrictions, saying there is nothing to indicate those moves will be necessary in the coming months, despite the fact Britain is experiencing a dramatic surge in COVID-19 infections.
Russia is preparing for or a weeklong workplace shutdown and the reimposition of a partial lockdown because of a surge in COVID-19 infections and deaths.
Daily coronavirus deaths in Russia have been rising for weeks because of sluggish vaccination rates, casual attitudes toward precautionary measures and the government’s hesitance toward tightening restrictions. The country’s national task force on COVID-19 said only about one-third of Russia’s 146 million people have been vaccinated, straining the country’s health system.
Russian President Vladimir Putin said last week that employees would observe “non-working days” from October 30 to November 7, during which they would still receive salaries. He said the period, in which four of the seven days are state holidays, could start earlier or be extended in certain regions.
The rollout of Russia’s Sputnik V COVID-19 vaccine in Namibia was postponed Saturday by the country’s health ministry after the vaccine’s regulator in neighboring South Africa raised concerns about its safety for people at risk of HIV.
The regulator said it would not approve an emergency-use application for the vaccine at this time because some studies suggest that the delivery system, known as a vector, used to inoculate people with the Sputnik V vaccine can cause men to be more susceptible to HIV.
The vaccine’s manufacturer, Gamaleya Research Institute, said Namibia’s postponement was not based on scientific evidence.
The Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center reported early Sunday a global count of 243.3 million COVID cases and almost 5 million COVID deaths. The center said 6.7 billion vaccines have been administered.